Cardiothoracic Surgery
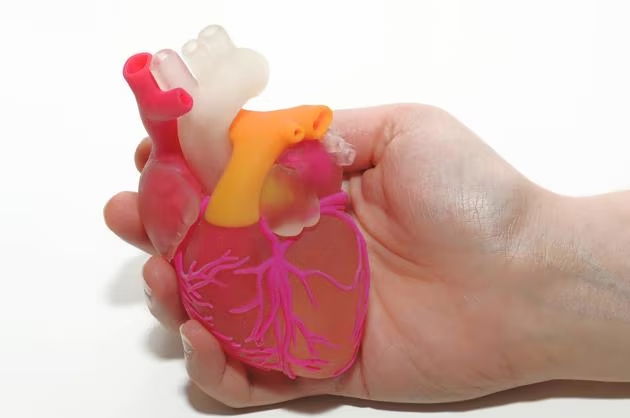
Cardiothoracic surgery is a specialized branch of surgery that focuses on the treatment of conditions affecting the heart, lungs, esophagus, and other organs within the chest cavity. 3D printing has emerged as a powerful tool in this field, allowing cardiothoracic surgeons to enhance their surgical planning, simulate complex procedures, and improve patient outcomes.

Valve Replacements: 3D-printed heart models can accurately replicate the complex anatomy of the heart, including valves. Surgeons can use these models to simulate valve replacement procedures, such as replacing a damaged heart valve with an artificial one. These simulations enable surgeons to practice different approaches, choose appropriate valve sizes, and refine their techniques before the actual surgery

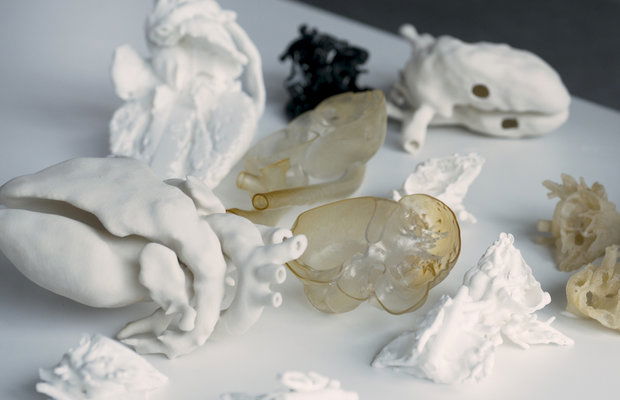
Minimally Invasive Procedures: Some cardiothoracic procedures are performed using minimally invasive techniques, such as robotic-assisted surgeries. 3D-printed models aid surgeons in practicing these procedures, allowing them to refine their skills in instrument manipulation and navigation within a controlled environment.
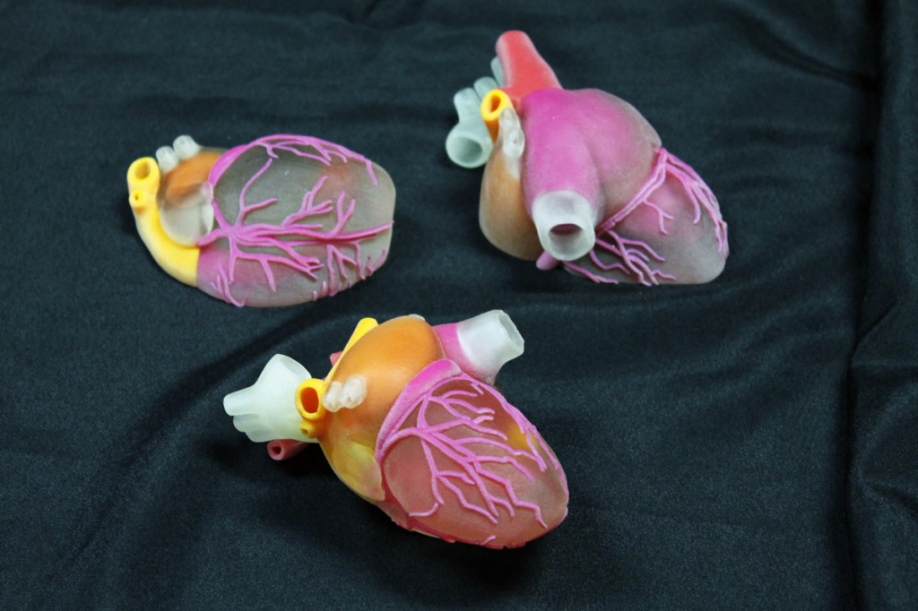
Patient-Specific Approach: Every patient's cardiac anatomy is unique. 3D printing enables the creation of patient-specific heart models, which allow surgeons to tailor their surgical approach based on the individual's anatomy. This customization enhances surgical precision and contributes to better outcomes.
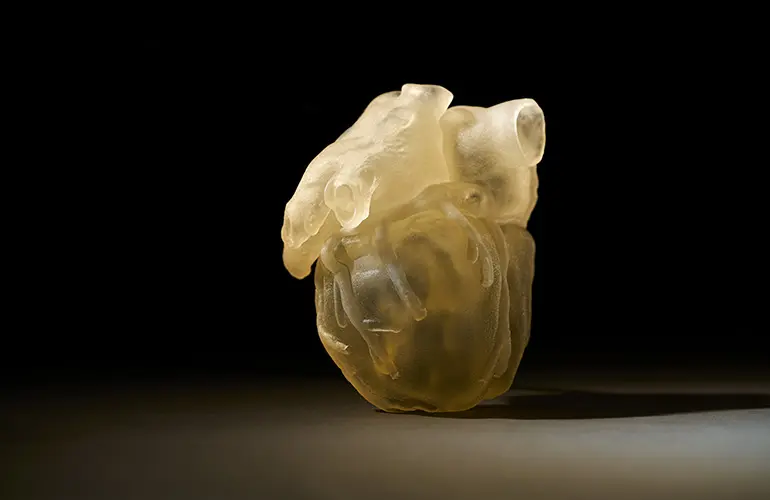

Education and Communication: 3D-printed heart and lung models serve as valuable educational tools for medical students, residents, and patients. These models help explain complex cardiac conditions and procedures in a visual and tactile manner, enhancing understanding and informed decision-making.

Innovation and Research: Cardiothoracic surgeons and researchers can collaborate to develop innovative surgical techniques, devices, and approaches using 3D-printed heart and lung models. These collaborations can lead to advancements in the field and improved patient care. In summary, 3D printing has revolutionized cardiothoracic surgery by providing a realistic and customizable platform for surgical planning and simulation. By utilizing 3D-printed heart and lung models, surgeons can practice complex procedures, enhance their skills, and optimize their approaches, ultimately leading to improved outcomes for patients with heart and lung conditions.


